Hartlepool Local Authority Area – Summary Description of the Natural Environment
The borough of Hartlepool, the northernmost of the five boroughs of the Tees Valley, has an extensive stretch of coastline with the North Sea as its eastern boundary, and borders the County of Durham to the west and the borough of Stockton-on-Tees to the south. It is covered by two of Natural England’s National Character Areas (NCA): the Tees Lowlands to the south and the Durham Magnesian Limestone Plateau to the north. The eastern half of the borough is dominated by urban settlement with some of the heavy industry of the Tees Valley in the south east at Teesmouth, on the estuary of the River Tees. In sharp contrast, the western half of the borough is open countryside with mostly intensively farmed arable land, some pasture and a network of hedgerows. Two main beck systems, Greatham Beck and Claxton Beck, drain the broad low lying plain of the Tees Lowlands. Both flow into Greatham Creek, which forms the southern boundary with Stockton-on-Tees.
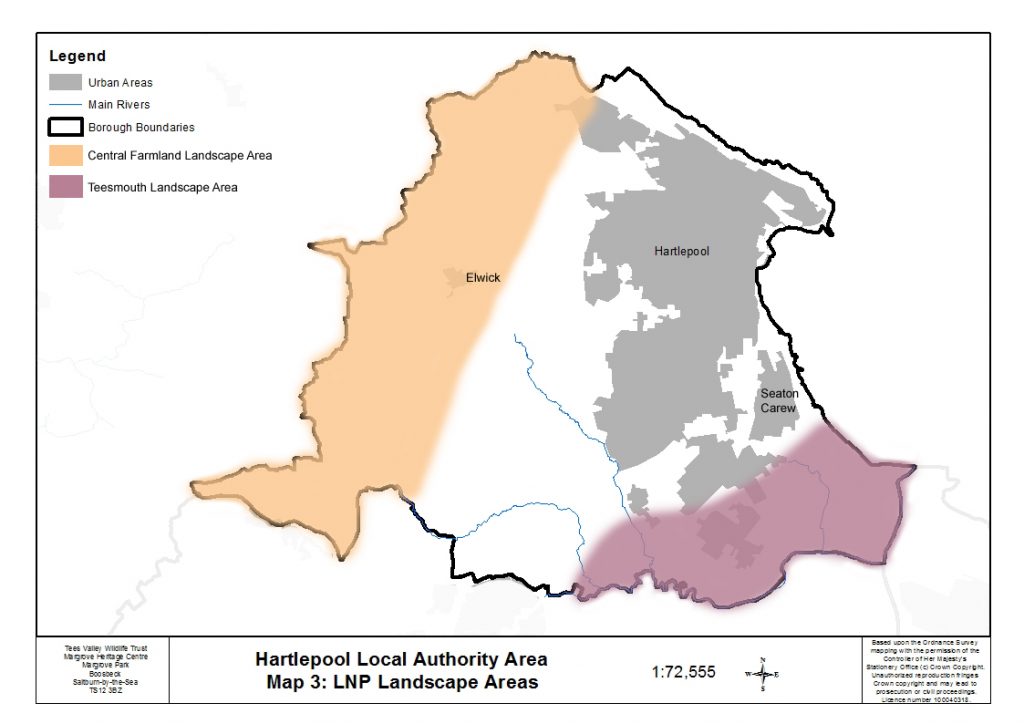
Two of the five Tees Valley Nature Partnership Landscape Areas fall partly within the borough of Hartlepool, Teesmouth and Central Farmland.
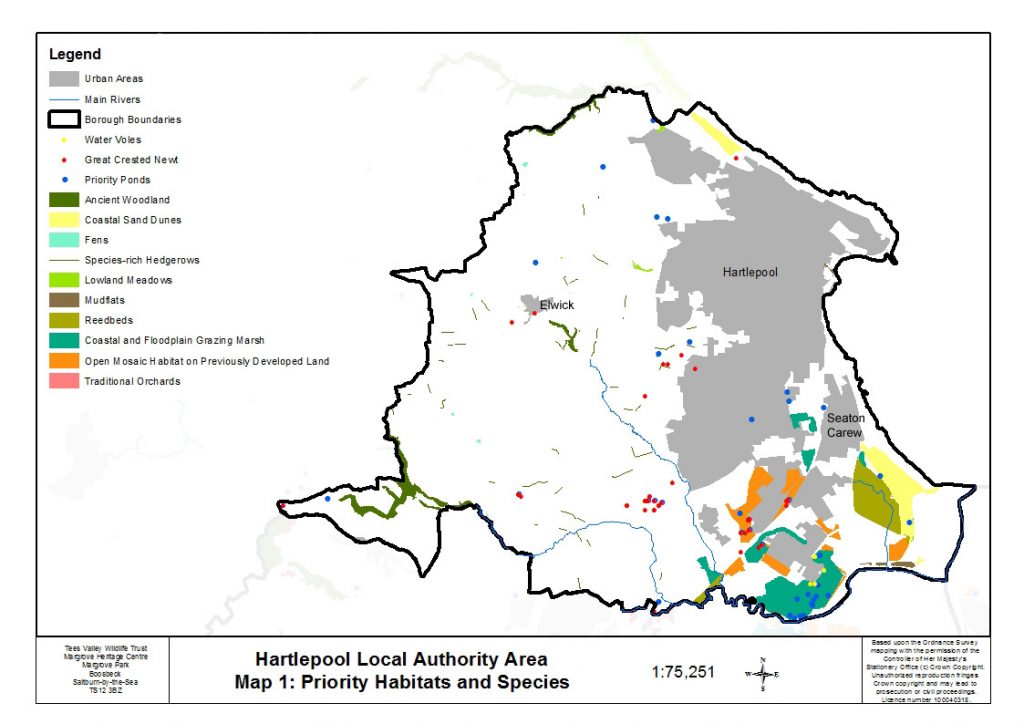
Hartlepool borough contains a number of priority habitats and species, mostly concentrated within Teesmouth but also along the coastline and scattered across the open farmland.
Teesmouth is a mosaic of estuarine habitats mostly reclaimed over the last two centuries for industry but still containing remnants of estuary-related habitats such as mudflats, coastal and floodplain grazing marsh and sand dunes along with open mosaic habitat on previously industrial land (formerly known as brownfield sites). It includes sites of international importance for over-wintering and breeding wildfowl and wetland birds and some of these sites lie partly within the Hartlepool area. There are several areas of coastal and floodplain grazing marsh within the Teesmouth area of Hartlepool, the largest being at Greenabella Marsh and Seaton Common; Seaton Common also has a large area of sand dune. Mudflats are found along the north banks of Greatham Creek and Seaton Channel (part of the large intertidal mudflats at Seal Sands), and at West Harbour. Remnants of salt-marsh occur along the north bank of Greatham Creek, within the Seaton Dunes and Common SSSI, and at the Slake, close to Victoria Harbour. Areas of reed-bed are found at Seaton Common and Cowpen Marsh. Open mosaic habitat is found centred upon areas which were formerly subject to land reclamation. Several of the sites consist of open mosaic grassland, supporting important butterfly species, whilst the remainder support important amphibians.
The coastline features stretches of dune systems, sandy beaches, coastal grassland and important geological features. The coastline from Crimdon Dene to Hartlepool Headland supports internationally important populations of wildfowl and wetland birds and West Harbour and Carr House sands are important for overwintering bird populations. Sand dune systems are found at Hart Warren dunes, which support many plant species characteristic of both northern and southern British dune systems, and Seaton Dunes, which is the largest sand dune system between Lindisfarne to the north and the Humber to the south. Seaton Dunes and Seaton Common link the habitats of the coastline with those in Teesmouth.
Habitats found scattered across the open farmland include woodland, grassland, fens, ponds, hedgerows and orchards. Ancient and semi-natural woodland is found in Hesleden Dene on the northern boundary with Durham and at The Howls near Elwick. The Wynyard Woodland Park Complex in the south west of the borough contains some ancient and semi-natural woodland, along with broadleaved mixed woodland and one site of wet woodland. Hedgerows are a feature across the open farmland and some of them have been found to be species-rich. There is a cluster of small lowland meadows around Elwick, whilst other neutral grasslands that are species-rich are found scattered across the open farmland, mostly associated with slopes. Also across the farmland are six fens, the most important being Hart Bog SSSI. Two traditional orchards are present in the north west, close to the boundary with Durham.
Priority ponds are mostly found in the urban and industrial areas of Hartlepool, with a few isolated ponds scattered across the farmland. The majority of the ponds meet the priority pond criteria due to the presence of either common toad, great crested newt or water vole.
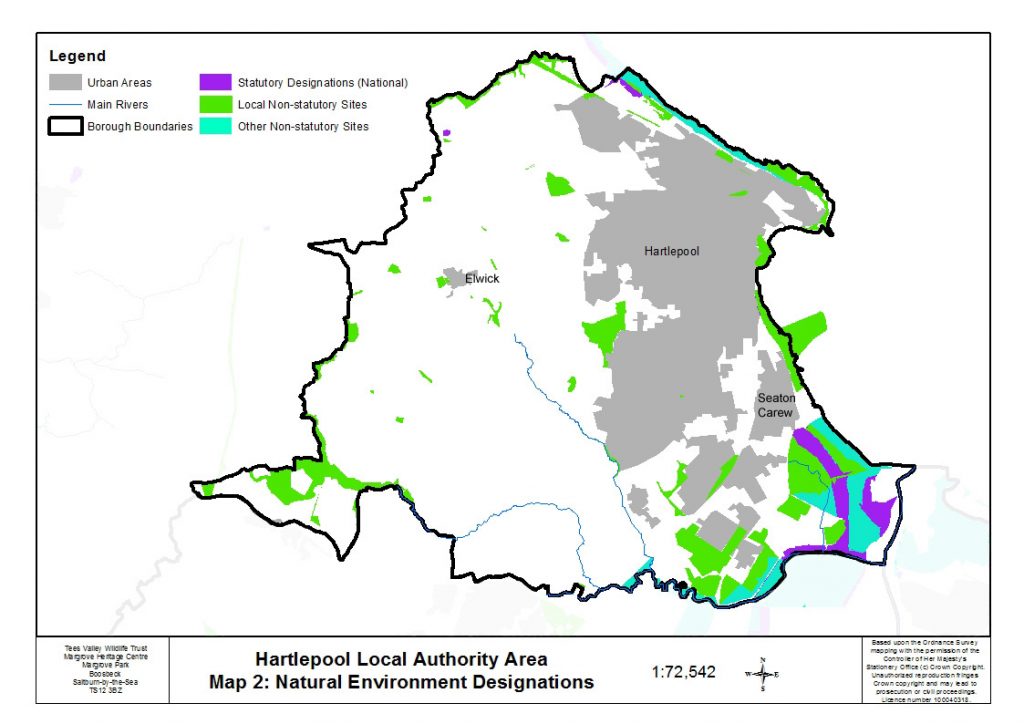
The coastline has several important geological features: Hartlepool Submerged Forest, Hartlepool Headland and Long Scar and Little Scar. Across the farmland there are two important geological sites, one at Dalton Batts and one at West Crimdon Dene, and also four quarries, all showing important geological features, two of which are recolonising with grassland and scrub.
Populations of great crested newts are found at Summerhill, Claxton, and within the industrial area north of Greatham Creek. Water vole is present at Greenabella Marsh and Phillips Tank Farm in the industrial area, and along the Greatham Beck corridor west of Hartlepool.
Breeding populations of bird species of key importance in the Tees Valley are present within the farmland to the west of Hartlepool. Species listed as of red level of concern in the UK include yellowhammer, cuckoo, corn bunting, yellow wagtail; species listed as of amber concern in the UK include quail, green woodpecker, redstart and bullfinch. Most of these species are also UKBAP priority species. The entire wintering population of little egrets from Teesmouth nest at Rossmere Park. Most of the coastline is important for non-breeding/overwintering bird populations, including the area around the estuary which has international and national designations for winter populations of water birds including non-breeding populations of red knot, common redshank and sandwich tern.
Common Lizard has been recorded at Hartlepool Power station, Greenabella Marsh, North Hartlepool Dunes and Hart to Haswell railway. Dingy skipper and grayling butterflies are found at sites within the industrial area; grayling is also found at Hart to Haswell Walkway.
Crookfoot Reservoir supports good numbers of bats (four species have been recorded including nathusius pipistrelle and noctule). Harvest mouse is present at Butts Lane. There is a population of harbour seal centred upon Seal Sands and they often move along Seaton Channel and haul out along Greatham Creek. They are also regularly present just offshore along the coastline of Hartlepool and regularly seen in the entrance to Victoria Harbour.